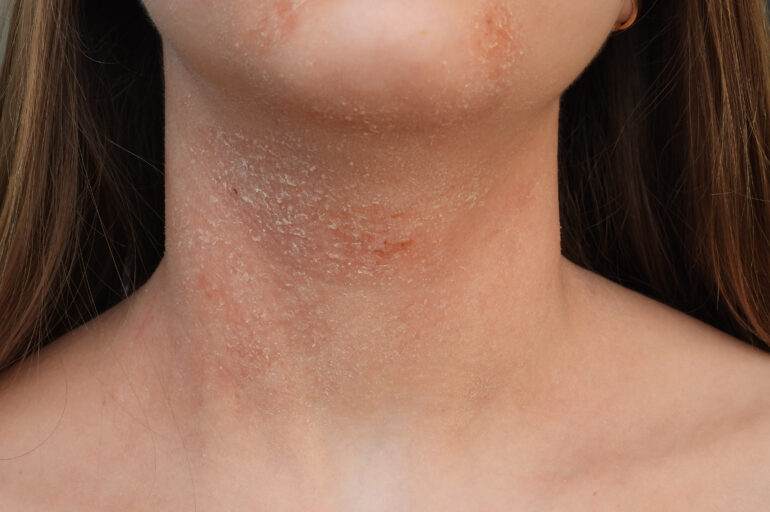
Atopic dermatitis and stress are two interconnected conditions that affect a significant number of people around the world. While atopic dermatitis involves chronic inflammation of the skin leading to itching and redness, stress can play a key role in its exacerbation and persistence. The complex relationship between these two factors has sparked growing interest in the medical and scientific community, which seeks to understand how stress can trigger and worsen the symptoms of atopic dermatitis, as well as therapeutic strategies that can address this interaction. In this article, we will thoroughly explore the connection between atopic dermatitis and stress in addition to proposing some treatments that we believe can be effective for people who are experiencing this condition.
What is stress dermatitis?
Stress dermatitis is a skin condition that can be triggered or worsened by emotional or psychological stress. It often manifests as a skin rash that can be red, itchy, scaly, or even blistered. This condition is considered an inflammatory skin disease and can affect people of all ages.
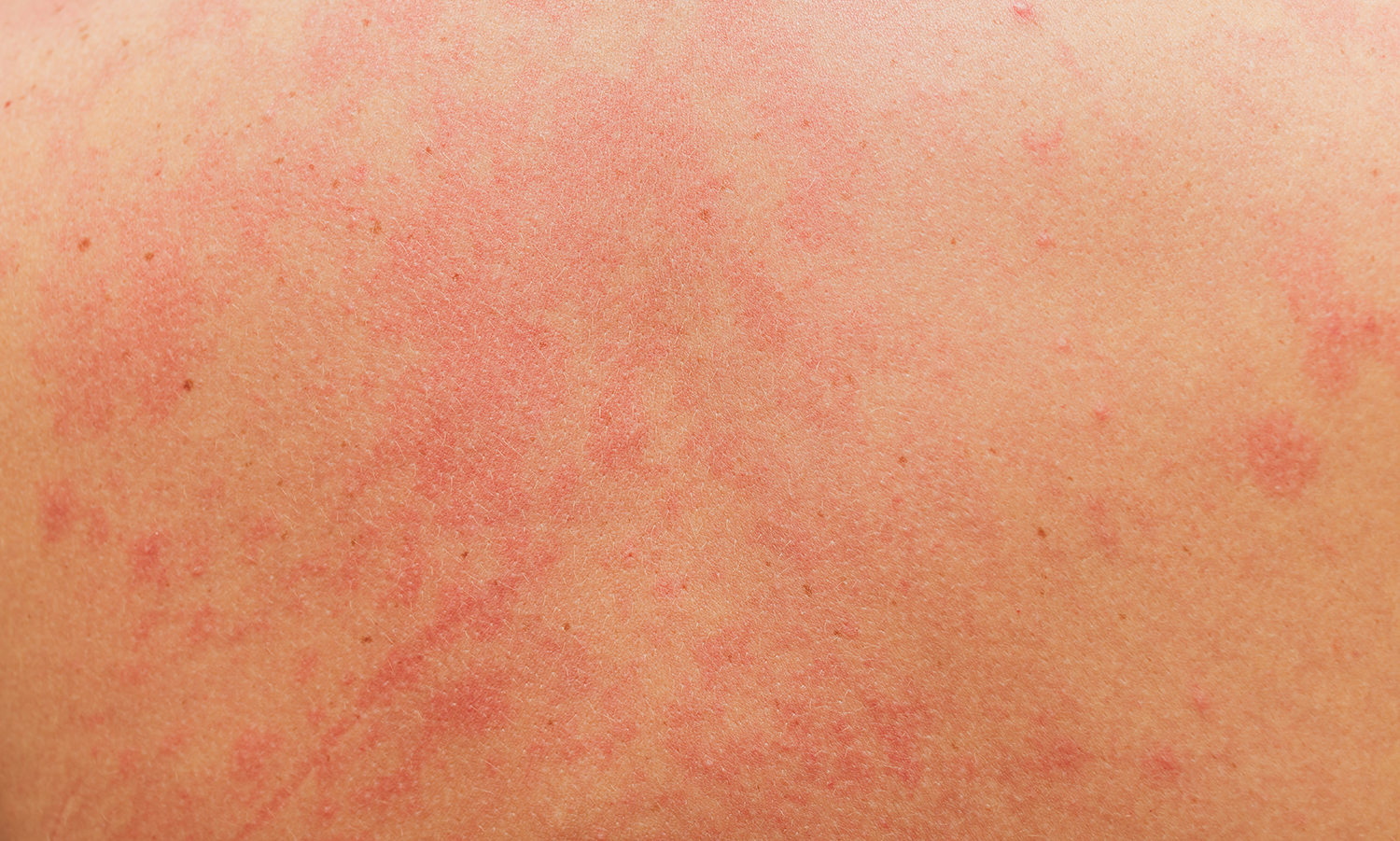
Chronic stress can trigger a number of physiological responses in the body, including the release of hormones such as cortisol, which can impact the immune system and skin health. While stress dermatitis can manifest in different ways in different people, it is important to address both the underlying cause of stress and treat the skin symptoms to achieve complete relief.
Symptoms of stress dermatitis
Symptoms of stress dermatitis can vary from person to person, but commonly include:
- Redness in the skin.
- Intense itching.
- Skin rashes that may be scaly or blistered.
- Dry and cracked skin.
- Excessive skin sensitivity.
- Irritation and burning sensation on the affected skin.
- Inflamed and sensitive skin to the touch.
These symptoms usually appear in specific areas of the body, such as the face, scalp, hands, and feet, although they can spread to other parts of the body depending on the severity of the condition. Additionally, prolonged stress can worsen these symptoms and lead to recurrent outbreaks of stress dermatitis. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek the guidance of a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Treatments for eczema and atopic dermatitis due to stress
Stress management through relaxation techniques, exercise, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, psychological therapy, may be beneficial in reducing the severity and frequency of stress dermatitis flares. Additionally, topical treatment with creams or those prescribed by a doctor specializing in dermatology can also help control skin symptoms. In addition to all this, we leave you some recommendations so that you can avoid when you have a reaction due to eczema or atopic dermatitis:
- When bathing or showering, make sure the water is not too hot, as this could further irritate your skin.
- Don’t bathe more than once a day and use a mild, unscented gel.
- Apply a perfume-free, toxic-free moisturizer immediately after showering.
- Avoid very high or humid temperatures.
- Use 100% cotton clothing and wash it with ecological detergents , without using fabric softeners.
- Eat a balanced diet that contains nutritious foods
- Do sports that will help reduce stress
- Hydration is the key because dry skin is a trigger for atopic dermatitis or eczema.
How to prevent stress dermatitis
Stress dermatitis is a skin condition that can be triggered or worsened by stress factors. Here are some tips to prevent stress dermatitis:
- Stress Management: Learn stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and regular exercise. These practices can help reduce anxiety and stress, which in turn can reduce dermatitis flare-ups.
- Skin care: Keep your skin well hydrated and use gentle, fragrance-free products that are suitable for your skin type. Avoid products that contain irritating ingredients that can worsen dermatitis.
- Healthy diet: Maintain a balanced, healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods that may trigger allergic reactions or worsen dermatitis.
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid known triggers that can worsen your dermatitis, such as certain foods, detergents, chemicals, and allergens.
- Adequate rest: Make sure you get enough sleep every night and maintain a regular sleep schedule. Adequate sleep can help reduce stress levels and improve skin health.
- Regular exercise: Exercise regularly as it can help reduce stress levels and improve overall health, including skin health.
- Emotional support: Talk to friends, family, or a mental health professional if you feel like stress is affecting your emotional well-being. Emotional support can help reduce the burden and impact of stress on your life.
Vitae solution
At Vitae we care about your health and that is why we have developed some products that will help you avoid atopic dermatitis due to stress.
OlioVita , a food supplement based on sea buckthorn oil, a revolutionary ingredient rich in omegas 7,3,6 and 9 that will help you nourish, hydrate and repair the skin from the deepest layers of the skin. This means that if you have any eczema triggers, OlioVita will be your ally to help make any topical treatment more effective.
OlioVita Repair repairing moisturizing balm developed for extremely dry or atopic skin. It will help you relieve problems related to atopic dermatitis, helping to reduce the associated inflammation. Helps wound healing and collagen production. It contributes to tissue repair processes in addition to providing antimicrobial activity to avoid infections during healing. It relieves itching and restores the barrier function, repairing the integrity of damaged skin, all thanks to its content of sea buckthorn oil, centella asiatica extract, mallow extract, argan oil, sesame oil, hyaluronic acid and soothing peptides.
ReConnect is our most innovative product thanks to its formula that will help you keep your mood at bay and control stress, thanks to its content in NADH, Coenzyme Q10, Serine and Vitamin C.