Immunity, a complex and highly coordinated system, is essential to protect us from viruses, bacteria and other intruders that could compromise our health. This article, written by Luisa Varela , technical director of Vitae, gives a deep introduction into the fascinating world of immunology , exploring the different types of immunity that the body deploys to keep us resistant to a vast spectrum of threats.
What types of immunity exist?
There are several types of immunity, which are mechanisms by which the body defends itself against pathogens and foreign substances. Here are some main types:
Innate Immunity
It is the body’s first line of defense and acts quickly and generally against any pathogen. It includes physical barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes, as well as phagocytic cells that ingest and destroy invading microorganisms.
Adaptive or Acquired Immunity
It develops throughout a person’s life and is specific for each pathogen. It includes humoral immunity, mediated by antibodies produced by B cells, and cellular immunity, mediated by T cells that can destroy infected cells.
Active Immunity
Occurs when the body’s immune system produces its own immune response, either through natural infection or vaccination. After exposure to a pathogen, the body develops immunological memory for a faster response in the future.
Passive Immunity
It is acquired through the transfer of antibodies or immune cells from one person to another. It can occur naturally, such as the transfer of antibodies from a mother to her baby during pregnancy or breastfeeding, or artificially through the administration of specific antibodies (vaccines).
What types of immunity can we modulate and how to do it?
Immunity modulation involves influencing the response of the immune system to achieve a specific response. Here are some approaches and ways to modulate immunity:
Immunization (Vaccination): One of the most effective ways to modulate immunity is through vaccination. Vaccines expose the immune system to specific parts of a pathogen or weakened versions of it, triggering an immune response. The resulting immunological memory allows for a faster and more effective response in the event of future exposure to the pathogen.
Immunosuppressive Therapy: In some cases, it is necessary to reduce the body’s immune response, such as in the case of organ transplants, where immunosuppressive therapy is used to prevent rejection of the transplanted organ. However, this strategy carries a risk of increasing susceptibility to infections.
Immunotherapy: Also known as biological therapy, immunotherapy involves the use of immune system components or substances designed to modulate the immune response. It is used in the treatment of certain types of cancer and autoimmune diseases. For example, immune checkpoint inhibitors stimulate the immune response against cancer cells.
Immune Cell Stimulation: Some compounds can directly stimulate certain cells of the immune system. These compounds may include cytokines, which are proteins that regulate the immune response. Cytokine therapy has been used in the treatment of certain types of cancer.
Dietary Modulation: Diet may also play a role in modulating immunity. Nutrients such as vitamins and minerals are essential for the proper functioning of the immune system. A balanced diet rich in these nutrients can help maintain a healthy immune response.
Probiotics : Probiotics , which are health-beneficial microorganisms, can influence immune function by modulating the composition of the intestinal microbiota . This can have positive effects on the overall immune response, since the immune response begins in the intestine.
Food supplements: can they be useful to strengthen the immune system?
Yes, some dietary supplements can be useful in boosting the immune system, especially in situations where there may be nutritional deficiencies or in people with compromised immune systems. Here are some nutrients and supplements that have been associated with supporting immune function:
Vitamin C: It is an antioxidant that has been associated with stimulating the production and function of white blood cells. It is found in citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, peppers and other foods.
Vitamin D: Plays a crucial role in immune function and is obtained primarily through sun exposure. However, in cases of deficiency, vitamin D supplements may be beneficial.
Zinc: This mineral is essential for the function of white blood cells and other components of the immune system. It is found in meats, nuts, whole grains and dairy products.
Probiotics : Probiotic supplements can help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut, which in turn can influence immune function.
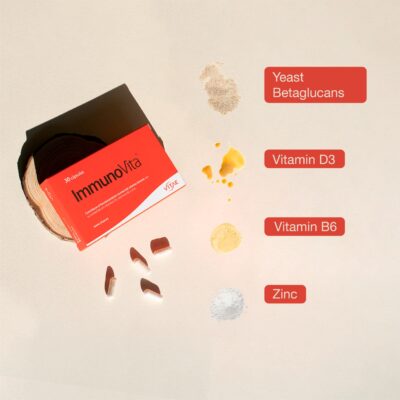
Beta glucans : Betaglucans are polysaccharides found in the cell walls of certain microorganisms, such as yeast, algae and some fungi. It has been researched and suggested that betaglucans , especially those derived from yeast, may have immunomodulatory properties , meaning they can modulate the response of the immune system.
Additionally, maintaining healthy lifestyle habits, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management, is also essential for maintaining a strong immune system.
Vitae solution
We present our star seasonal product ImmunoVita, a reference food supplement that will help you strengthen your defenses, helping to reduce tiredness and fatigue and will also help you defend yourself against virus infections, thanks to its content of yeast beta- glucans, vitamin D3, B6 and zinc.