Urinary infections are very common, especially in women, they can be quite annoying and painful. Having a good habit of intimate hygiene will be essential when trying to prevent and treat this type of infection. You will also have to be aware of some behaviors, such as sexual relations, that can lead to the presence of this infection. In this article we tell you more about urine infections and sexual relations, and how they are related.
What is a urine infection
It is an infection that can happen in any part of the urinary system, whether in the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Although it is more common to occur in the lower urinary tract, bladder and urethra. Anyone can suffer from a urinary tract infection, although it is usually more common in women.
Types of urine infection
There are two types of urinary infections: cystitis and urethritis.
Cystitis
It is an infection that affects the bladder. It is the most common infection of the urinary system and the entire body after respiratory infections. Most of the time cystitis occurs when there is an infection caused by bacteria, although it can also happen due to a virus, fungi or parasites. Many of them are to blame for the Escherichia bacteria. coli , normally lives in the intestine. The most common symptoms of cystitis are:
- Constant need to urinate
- Painful and burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent urination in small amounts
- Blood in the urine
- Cloudy urine and strong odor
- Pelvic discomfort
- Feeling of pressure in the abdomen
- Slight fever
Urethritis
It is inflammation of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the body. This infection can be caused by bacteria or viruses. Being a woman can be a risk factor when it comes to suffering from urethritis, as well as being a man between 20 and 35 years old. Another factor could be having multiple sexual partners, high-risk sexual behavior such as not using a condom, or a history of sexually transmitted diseases.
The most common symptoms are:
In women:
- Abdominal pain
- Burning pain when urinating
- Fever and chills
- Pelvic pain
- Vaginal discharge
- Pain during sexual relations
In men:
- Blood in urine or semen
- burning pain when urinating
- Penis discharge
- Frequent or urgent urination
- Penis tenderness, itching, or swelling
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area
- Pain during sexual intercourse or ejaculation
Both infections, if not treated properly, can spread and cause a kidney infection. Some of the symptoms would be pain in the middle of the back, fever, nausea and vomiting. That is why, although urinary infections are very common, we must not forget to treat them and take them seriously.
Diagnosis of urine infection
- Testing a urine sample: Your urine will be tested for white blood cells, red blood cells, or bacteria.
- Culture of bacteria from the urinary tract in a laboratory: from this test we know which bacteria are causing the infection, in addition to determining which medications will be most effective.
- Imaging of the urinary tract: The professional may order an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to see if there are any anatomical problems in the urinary tract. A contrast dye may also be used to highlight the structures of the urinary tract.
- Using an endoscope to look inside the bladder: a cystoscopy will be performed. In this test, a long, thin probe with a lens is used to look inside the urethra and bladder.
Can having sexual intercourse cause urine infection?
According to the Cystitis Information Center, sexual intercourse increases the chances of suffering from urinary tract infections.
- Sexual relations favor the entry of bacteria: during sexual practice, the man contributes to the colonization of the woman’s urinary tract, being “pushed” into the female body.
- Sex involves trauma to the vagina and urethra: it can be trauma, due to the impact produced by the penis through the vagina, which weakens the female urinary system, contributing to the colonization of the Escherichia bacteria. coli .
- Oral contraceptives weaken the bladder mucosa: the hormones contained in oral contraceptives weaken the bladder mucosa, modify the menstrual cycle, help prevent pregnancy and facilitate colonization by the Escherichia bacteria. coli , responsible for urinary infections.
- Condoms modify the mucous membranes of the vagina and bladder: they contribute to the development of urinary tract infections, or cystitis.
- Proper intimate hygiene: empty the bladder before and after having intercourse: not maintaining adequate intimate hygiene and not emptying the bladder before and after having intercourse facilitates the development of infections. Drinking plenty of water will help increase the amount of urine and therefore help eliminate bacteria lodged in the bladder.
Can I have sex if I have a urine infection?
You can have sexual relations even if you have a urinary tract infection, but it is highly advisable to avoid it, as it can worsen the symptoms of the infection and become a painful activity. It is estimated that 60% of recurrent cases of cystitis are explained exclusively by having sexual relations.
Treatments for urine infection
At Vitae we care about your health and that is why we try to offer the best of us, providing valuable ideas for your daily life. Many times, to achieve full well-being, supplementation is necessary, and below we tell you our proposal: UrinVita and ImmunoVita .
UrinVita It is a natural food supplement based on pomegranate extract, grape extract, cranberry and rosemary. Thanks to its content of proanthocyanidins and procyanidins, it contributes to the well-being of the urinary system. Its set of ingredients has an antibacterial, antioxidant, antimicrobial effect and even helps break down and prevent the adhesion of bacterial biofilms .

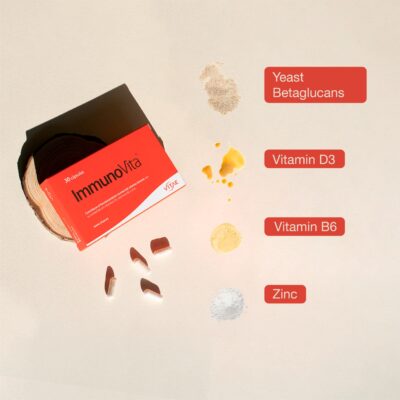
ImmunoVita is a natural food supplement based on latest generation yeast beta-glucans , vitamin D3, vitamin B6 and Zinc. The synergy of these components contributes to the normal functioning of the immune system, helping to reduce tiredness and fatigue, and to protect cells against oxidative damage.