The good condition of a woman’s intimate area is achieved through specific care, since it is very sensitive, and with the slightest change, the pH of the flora is altered and this leads to increased risk of an infection or other pathologies. In the following article we will talk about one of the infections that can occur in the intimate area, vaginitis, along with its symptoms and treatment.
What is vaginitis?
Vaginitis or also called vulvovaginitis is defined as an inflammation or infection in the mucosal wall of the vagina. The vulva, the external area of the woman’s genitals, may also be affected. It is common, especially in women of reproductive age. It is diagnosed in more than 25% of patients who go to the gynecologist and it is estimated that 90% of women suffer from some type of vaginitis throughout their lives. It usually happens when there is a change in the balance of bacteria or yeast that is normally found in the vagina.
Types of Vaginitis
Bacterial vaginosis
It is the most common vaginal infection, it can occur at any age, but it is more common during the reproductive years and in sexually active people. It happens when there is an imbalance between the good and bad bacteria normally found in a woman’s vagina. The most common symptoms are:
- Unusual vaginal discharge.
- Strong odor in vaginal discharge.
- Itching or irritation around the vagina.
- Burning sensation when urinating.
There are risk factors when contracting this infection. Having different sexual partners or a new sexual partner can be a reason for infection, although it is not 100% related. Vaginal douching can also cause this infection, since the vagina cleans itself and it is not necessary to rinse it with water or other products. They can alter the healthy balance of bacteria in the vagina. And finally, there may be a natural absence of lactobacilli . If the vagina does not produce enough, infection is likely to occur.
Vaginal candidiasis
It is a vaginal yeast infection caused by the overgrowth of a fungus called Candida albicans . The most common symptoms of this infection are the following:
- Pain and itching in the vagina and/or vulva.
- Pain, burning, and redness around the entrance to the vagina.
- Small swelling of the vaginal lips.
- White discharge similar to cottage cheese
There are other symptoms that are less common such as: pain during sexual intercourse, thick vaginal discharge, red and swollen vaginal lips, itching around the vulva and pain when urinating.
There are different causes that can give rise to vaginal candidiasis, such as : hormonal changes, changes in the vaginal bacterial flora and a decrease in the immune system.
Hormonal changes can contribute to the appearance of candidiasis. An unbalanced diet, stress, use of hormonal contraceptives, menopause, pregnancy or menstruation are factors that cause hormonal changes.
The vaginal bacterial flora is normally made up of Lactobacillus and protects the wall of the area. It also generates lactic acid that helps maintain vaginal pH. When the vaginal flora is altered, it is closely related to the fact that there has been a change in pH, which causes vaginal infections to arise.
The immune system is essential to be in good condition for our entire body, in order to avoid infections. When this is seen at low hours, women are more likely to suffer from vaginal infections such as candidiasis.
Trichomoniasis
It is a common sexually transmitted disease caused by a parasite. Hormonal changes can also cause vaginal irritation. Symptoms in women:
- Abundant amounts of thin, sometimes unpleasant-smelling vaginal discharge
- Redness, burning and itching of genitals.
- Pain when urinating or having sex.
- Discomfort in the lower part of the stomach
Symptoms in man:
- Itching or irritation inside the penis.
- Burning sensation when urinating or after ejaculating.
- Discharge from the penis
As we have said before, this disease appears when there is genital contact, whether vaginal, oral or anal sex. The infection can be transmitted between men and women, between women and sometimes between men. Some of the risk factors that exist when contracting this infection could be: having multiple sexual partners, a history of sexually transmitted infections, having previously suffered from trichomoniasis or sexual relations without a condom.
Difference between vaginosis and vaginitis
Vaginosis occurs when the balance of bacteria in the vagina is altered and leaves this area exposed to become more prone to contracting harmful microorganisms and generating an imbalance in the vaginal flora . While vaginitis is a vaginal infection due to inflammation, burning and itching caused by allergic reactions, sensitivities to certain objects or substances, uncontrolled diabetes, long-term use of antibiotics, low defenses, etc.
Causes of vaginitis
There are many factors that can cause vaginitis, some of them may be:
- Common vaginal infections: vaginal yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis , or trichomoniasis.
- Lack of estrogen (atrophic vaginitis): when there is a lack of estrogen, a type of vaginitis called atrophic vaginitis or vaginal atrophy can appear. What happens is that the vagina is irritated, but the discharge is normal. Lack of estrogen can happen due to: breastfeeding, menopause, damage to the ovaries.
- Vaginal sex: Vaginitis is not a sexually transmitted disease, however it is possible that sex can cause you to get vaginitis. Your partner’s genitals have bacteria and fungi just like you, and when they are in contact there may be an imbalance and therefore alter the flora. Some lubricants, condom material or even friction can lead to vaginitis.
- Allergies and irritating products: We can have allergic reactions to materials or activities such as: douches, tampons, sanitary pads, perfumed bath products, certain lubricants, sex toys made of certain materials, latex, tight clothing, wet swimsuits And a long etcetera.
- Recurrent vaginitis: If you suffer from vaginitis 4 or more times a year, it is called “recurrent vaginitis.”
Main symptoms of Vaginitis
Vaginitis can appear from different causes, but usually they are the following:
- Irritation, inflammation, or changes in color of your vulva or vagina.
- Itching, burning and pain in the vulva or vagina.
- Pain and discomfort during sex.
- Urinating more often than usual.
- Vaginal discharge that is not normal
-
- Vaginal fungus: the discharge will be thick, white and odorless
- Bacterial vaginosis : greyish, foamy discharge with a fishy odor (although sometimes there are no symptoms).
- Trichomoniasis : foamy discharge, greenish-yellow color and bad odor, sometimes blood stains
-
There will be times when there are no symptoms, which is why it is much better to regularly observe how the vulva and vaginal discharge looks, feels or even smells, so that when it happens, you know if something is not going well.
How to prevent vaginitis
The best way to prevent vaginitis is to avoid anything that can upset the natural balance of the vagina. Each person is different, therefore, how they deal with infections will also be different. In any case, below we discuss some tips that can be carried out together, the same for everyone.
- Avoid using tampons and perfumed sanitary pads. Better not to use scented feminine hygiene products.
- Avoid using bath products, such as soaps or foam baths, that contain perfume.
- Avoid vaginal douching, since the only thing they do is kill the good organisms that maintain the balance of the vaginal flora. We must know that the vagina cleans itself, in any case, you can wash the vulva with a mild, unscented soap.
- Avoid having a wet vulva. Try to keep the intimate area dry, changing if you have a swimsuit and avoid wearing very tight pants.
- Change tampons and sanitary pads every 4-8 hours. Wash the menstrual cup and sex toys carefully.
- Clean yourself well after going to the bathroom, since the bacteria that are in the anus can spread to the vulva and cause a vaginal infection.
- Some lubricants can cause irritation, even the material of some condoms can cause allergies, therefore, other materials such as polyurethane, polyisoprene or nitrile should be used.
- You must know your genitals well. Observe well, and learn to recognize the normal odors and vaginal discharge in your intimate area. This is how you will end up discovering if you may be having an infection, since you will see changes in it.
At Vitae we care about your health and that is why we try to offer the best of us, providing valuable ideas for your daily life. Many times, to achieve full well-being, supplementation is necessary, and below we tell you our proposal: ImmunoVita and Vulbiotic .
Treatment of Vaginitis
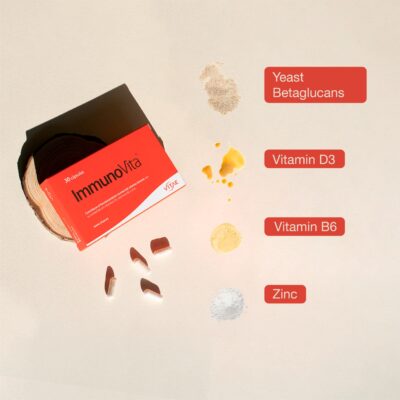
ImmunoVita is a natural food supplement formulated from latest generation yeast beta-glucans to increase defenses, strengthening the immune system naturally. It is composed of beta-glucans , vitamin D3, vitamin B6 and Zinc, ingredients that contribute to the normal functioning of the immune system, helps reduce tiredness and fatigue and protect cells against oxidative damage.

Vulbiotic is a food supplement based on Lactobacillus rhamnosus , Lactobacillus crispatus and Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) that contribute to restoring the vaginal microbiome , favoring the balance of the vaginal microbiota and its role as a natural barrier against genitourinary infections